| |
|
|
|
|


|
|||||
 |
|||||
 |
|||||
 |
The Energy Efficiency Labelling Scheme has been extended to petrol passenger cars.
LPG
VEHICLE SCHEME
This
scheme is one of a number of government initiatives to reduce vehicle emissions
and improve overall air quality. EMSD plays a multilevel role, which includes
the approval and monitoring of the safe operation of LPG vehicles, filling
stations, and maintenance workshops as well as the authorisation of trained
LPG mechanics.
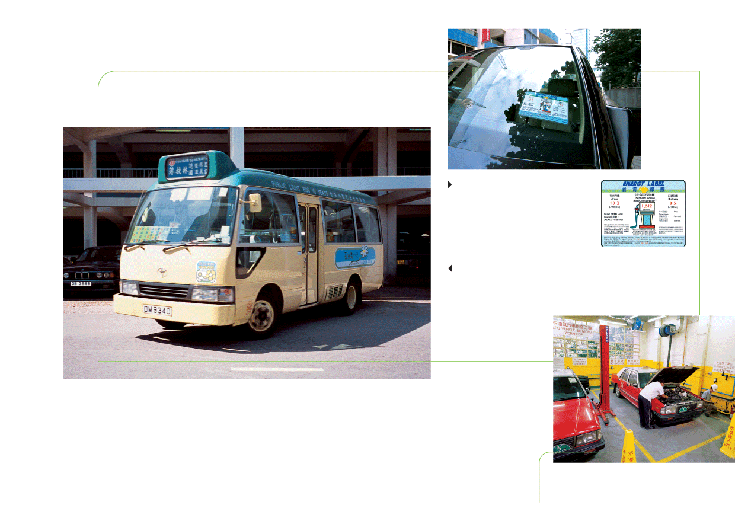
Almost 90 per cent of all diesel taxis
in Hong Kong have been replaced with LPG models. The scheme was extended to
light buses this year and there are currently more than 200 LPG light buses
on the road. Moreover, LegCo has approved a funding scheme as an incentive
for operators to switch to the more environment-friendly LPG or electric models.
At the time of writing, there were
already 43 auto-LPG filling stations, including 12 dedicated ones, in service
throughout the territory. EMSD provides expert advice on the ceiling price
mechanism for dedicated LPG filling stations, which has proven to function
satisfactorily. With dedicated filling stations leading the auto-LPG market,
the price of auto-LPG at all filling stations has been fairly stable despite
fluctuations in petrol and diesel prices.
Moreover, there are 28 LPG vehicle maintenance workshops in service, with
three more under construction. With regard to the authorisation of LPG mechanics,
there are about 800 trained mechanics registered with EMSD, and the Vocational
Training Council will continue to train 400 LPG mechanics a year to ensure
sufficient repair and maintenance support in the market.
The success of the scheme is reflected in the significant drop in pollutants of vehicle emissions - respirable suspended particulates and nitrogen oxide emitted by vehicles in the territory have been reduced by 25 per cent and 6 per cent respectively.
RENEWABLE
ENERGY
The first
stage of the consultancy study on potential applications of renewable energy
in Hong Kong is about to complete, with the aim of having various energy technologies
evaluated and an implementation strategy formulated.
The second stage consists of a demonstration project at Wanchai Tower, where
photovoltaic (PV) panels are being installed outside the building to test
the applicability of solar energy technologies in Hong Kong. Three types of
PV panels measuring 500 square metres are in use - rack-type on the rooftop,
sunshade screen-type on the external facade and skylight-type at the glass
entrance - and boast a total rated power output of 55 kW. Data will be collected
throughout 2003 to monitor the effectiveness and performance of the PV system.
Apart from investigating the application of solar PV technologies, EMSD will
also embark on a field-based wind measurement programme to explore the feasibility
of utilising wind energy at specific sites in the territory. Preparatory work
has commenced and the programme is scheduled for completion by mid-2004.