ENERGY
Tidal Energy
Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into electricity or other useful forms of power. Tides are changes in the level of the oceans caused by the gravitational attraction of the moon and the sun acting upon the oceans of the rotating Earth. The relative motions of these bodies cause the surface of the oceans to raise and lower periodically, according to a number of interacting cycles. The amount of energy obtainable from a tidal power plant therefore varies with location and time. Nevertheless, tidal energy is usually highly predictable in both the amount and the timing.
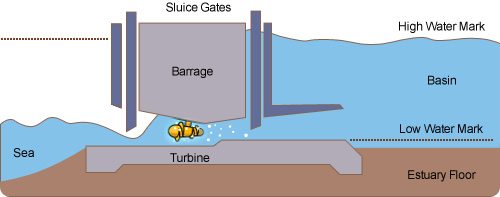
Tidal energy is the most promising source of ocean energy for today and the near future. Tidal energy plants capture the energy in the changing tides. A low dam, called a barrage, is built across an inlet. The barrage has one-way gates (sluices) that allow the incoming flood tide to pass into the inlet to create a water level difference. When the tide turns, the water flows out of the inlet through huge turbines built into the barrage, producing electricity.
Tidal Energy